MLSU researchers suggest Ramgarh Crater to be a Meteor impact site
Evidence has been found in a research conducted by a team from the Mohanlal Sukhadia University, which substantiates the arguments on the Ramgarh Crater at Baran in Rajasthan to be a meteor impact site and thus supports the call for declaring the site as National Geological Monument. Once substantiated, this will be a huge boost to tourism in the area
Evidence has been found in a research conducted by a team from the Mohanlal Sukhadia University, which substantiates the arguments on the Ramgarh Crater at Baran in Rajasthan to be a meteor impact site and thus supports the call for declaring the site as National Geological Monument. Once substantiated, this will be a huge boost to tourism in the area.
About the Ramgarh Structure
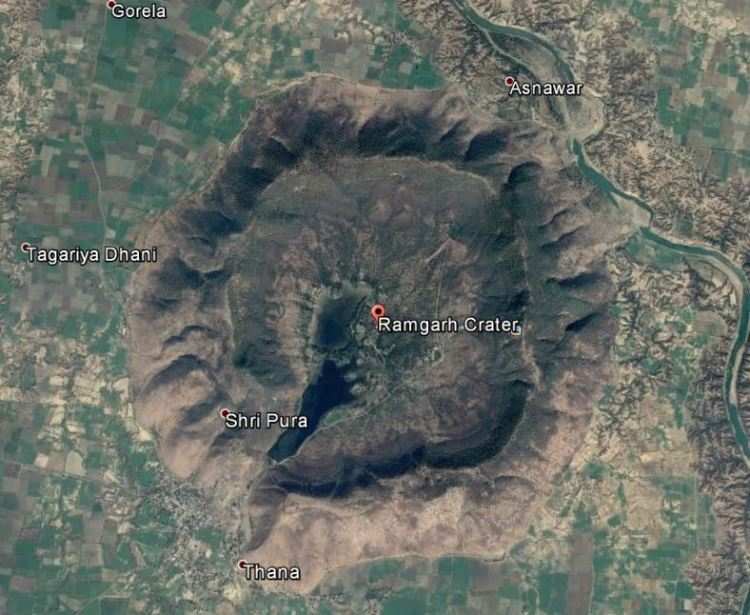
The origin of Ramgarh structure, which is a nearly circular regional geomorphic feature (with a diameter of 4 Kms) is a controversial matter among the Geoscientific community. It has been an impact crater in waiting for a long period of time and still deprived of the same designation due to the lack of unambiguous evidences of a meteorite impact. The Ramgarh Crater is situated in Baran district of Rajastha, 110 km East-North East of Kota (25º 20′ N: 76º 37′ E). The structure, which covers an area of 16 sqkm with a diameter of 4km, rising 250meter above the ground, resembles Meteor Crater of Arizona, USA, in terms of shape. This can be seen from a distance of 5-7km.

Aerial View of Lonar Crater

Ramgarh Crater visible from a distance of 5-7 km
At present, Lonar crater (Buldhana, Maharashtra) and Dhala crater (Shivpuri, Madhya Pradesh) are the only two confirmed impact craters in India.
An impact crater on the Earth is a depression that is formed by the high velocity impact of an extraterrestrial object like meteorite. Impacts produced on Earth are highly exposed to obliteration by various geological agents. This demands the use of certain diagnostic criteria for the identification and confirmation of impact structures on Earth, the most important of these are crater morphology, geophysical anomalies, evidences for shock metamorphism and the presence of meteoritic material. Microscopic features like Planar deformation features (PDFs) and Planar fractures (PFs) in quartz grains are uniquely diagnostic of an impact event and are the robust evidences of the shock metamorphism due to an impact.
A crater-like structure at Ramgarh, Rajasthan, India has been a contentious subject amongst the geoscientists for its origin. Evidences presented for the impact origin of Ramgarh structure so far are insufficient, equivocal and controversial.
Research and Evidence
Satyanarayan Rana, research scholar, under the guidance of Prof Vinod Agarwal of the Department of Geology, Faculty of Earth Sciences, Mohan Lal Sukhadia University, Udaipur, has completed a research to explore, evaluate and report the microscopic shock alteration evidences from the Ramgarh structure in the form of Planar Fractures and Planar Deformation Features in quartz grains.
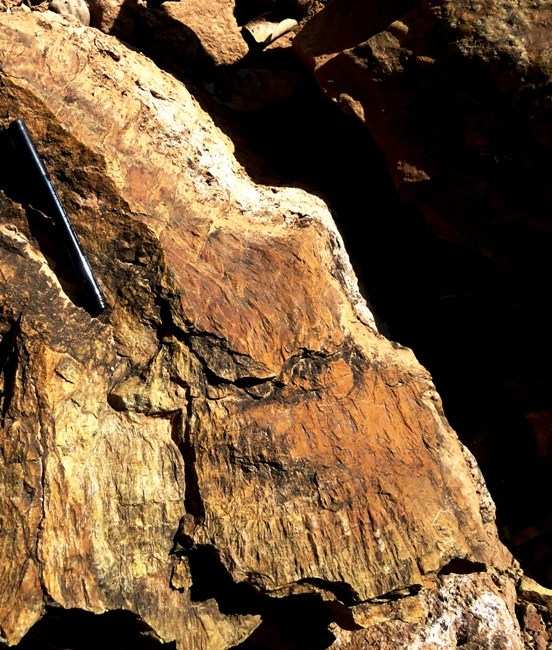

Shatter Cone
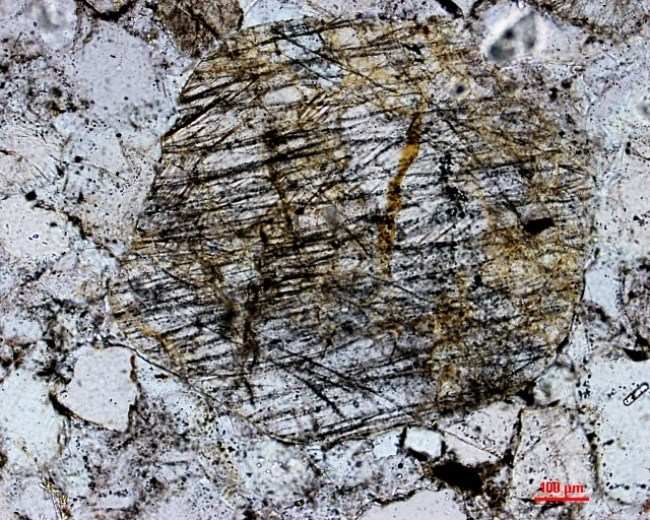

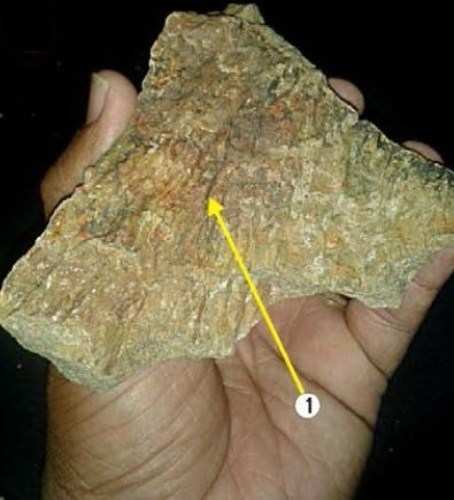
Quartz PFs
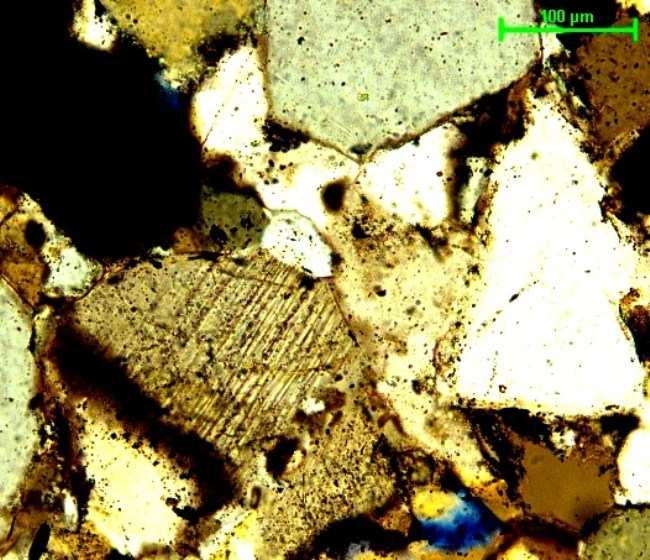

Quartz PDFs
The evidences found in the research work on Ramgarh structure strongly indicate its origin due to a meteorite impact. The evidences in the form of Shatter cones in sandstones (at megascopic scale) and Planar Deformation Features along with Planar Fractures in Quartz grains (at microscopic scale) are robust evidences of an impact event at Ramgarh since the development of these features have not been studied due to any of the endogenic processes operating on earth. They have been found only at impact sites worldwide. Their occurrence at Ramgarh, therefore strengthens the candidature of Ramgarh structure as an ‘Impact Crater’.
Earlier in January this year, a top official of the Geological Survey of India (GSI) had commented that the GSI is examining the prospects of declaring the Ramgarh crater in Baran, Rajasthan as a national geographical monument. The Ramgarh Crater has attracted many geologists since its discovery in 1869, by British researcher Mallet, on his first visit to the area. Later on, many geologists from different countries visited the area. This research has significantly impacted the prospects of the site being declared a National Geological Monument.
Petrographic observation of the sandstones collected from the centrally uplifted region by the authors have revealed the presence of shocked quartz grains marked by the significantly developed Planar fractures (PFs) as well as Planar Deformation Features (PDFs). Seven thin sections of sandstones that were examined are showing shocked quartz grains with well-developed parallel set of narrow open fractures. Three sets of planar fractures have been noticed which are not crossing grain boundaries. These fractures are widely spaced. The development of intense, widespread, and closely spaced planar fractures is strongly suggestive of shock, and such fractures are frequently accompanied in impact structures by other features clearly formed at higher shock pressures.
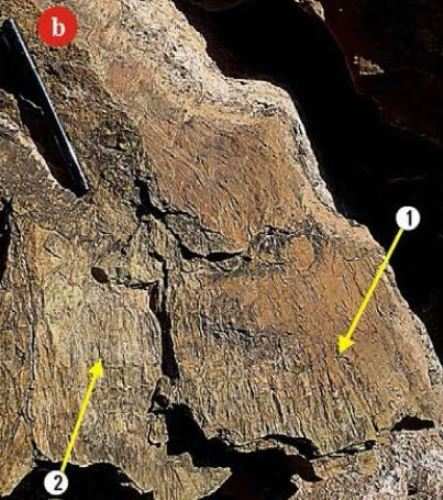

Shatter cones (1 & 2) in sandstone having well developed sub-conical to curvy planar striated surfaces forming a horse tail like pattern

Part of shatter cone showing well developed radial striation pattern

Shatter cone sample showing well developed broad striations with peeled off surface (1 & 2), topless cone in inner layer (3) and shatter cones with distinct apices pointing in same direction in inner layers (4 & 5).
During the course of research, detailed petrographic studies of the sandstone around the Ramgarh structure were carried out. Microscopic examination revealed the presence of Planar Fractures and Planar Deformation Features indicating shock metamorphism. Well-developed parallel set of narrow open fractures were noticed in the quartz grains exhibiting shock features. Owing to these diagnostic observations indicating shock metamorphism due to meteorite impact the impact origin of Ramgarh structure was inferred.

Slightly tilted sample (d) showing topless shatter cones (2 & 3) and shatter cones in inner part with apices (4 & 5)

Section of another shatter cone displaying the close up view of striations
The study conducted by research scholar Satyanarayan Rana under the supervision of Prof Vinod Agarwal, says that circular geological structures of regional extent like that one present at Ramgarh, which is located in geological setting with no other probable mechanism for creating near circular feature may be the result of a meteoritic impact and hence may be an impact crater.
This research was conducted as a part of the BSR Fellowship funded by UGC.
With inputs from: Satyanarayan Rana, IJFAR, IGU, Hindustan Times (Aerial Image of Ramgarh Crater)
To join us on Facebook Click Here and Subscribe to UdaipurTimes Broadcast channels on GoogleNews | Telegram | Signal


